How to set up Google Tag Manager

In this article, we’ll walk you through how to set up Google Tag Manager on your website. This is part 2 in our Measurement series of articles designed to help you track and act on data from your website. Other articles in this series cover setting up Google Analytics, installing Google Analytics into Google Tag Manager, and how to safely share access to both platforms.
What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager is a tag management system. It’s a way to quickly update measurement codes like tracking pixels without touching the code of your website. Back in the days before tag management systems, to place tracking or conversion pixels, you or your developer would have to add them all manually to your website code. Tag management systems changed all that. If you want to jump directly to how to set up Google Tag Manager, click here.
What sort of tags can you add to Google Tag Manager?
- Google Analytics
- Google AdWords
- Google Display Network
- and just about anything else you can imagine. If it’s a tracking tag, you can add it to Google Tag Manager.
With the insertion of a small segment of code on your website, Google Tag Manager places all the tracking and conversion pixels needed across your entire site. GTM handles the tracking tags themselves as well as all the triggering of the tags. All you need to do is place one segment of code, one time on your website and GTM does the rest. Now with Google Tag Manager in place you no longer provide website access to agencies. Instead, you provide access to your Google Tag Manager and your agency can add, modify, and remove measurement tags and triggers as needed. If you want to jump directly to how to set up Google Tag Manager, click here.
What’s a trigger in Google Tag Manager?
A trigger in Google Tag Manager tells a specific marketing tag to fire. When a tag fires, things happen. Here’s an example of how a Facebook tracking pixel might work on your site.
- A user visits your website
- Google Tag Manager runs and fires (activates) the Facebook Pixel to fire
- A cookie is placed by Facebook on the user’s computer
- This cookie adds the user to an audience on Facebook, this audience is ONLY available to you as “people who visited my website”.
- Now when the user visits Facebook, you can target them with advertising.
Of course, it’s a little more complicated than that, but you get the idea.

Triggers can run on every page, some pages, specific pages, or after certain events like clicks and the like.
Here are some samples of trigger events
- Pageviews
- Clicks
- Element visibility
- Form submissions
- History change
- JavaScript errors
- How far someone scrolled on your page
- Time-based
- And more
The trigger you use depends on what you want to accomplish.
Why use Google Tag Manager?
The reasons for using Google Tag Manager go beyond easier and faster implementation of marketing tags:
- Scalability across all pages on a single or multiple domains
- Manage multiple uses within GTM accounts
- Improved page load speed
- Triggers as described above

All in all, unless you have a really good reason not to use Google Tag Manager, you should be implementing marketing tags with it.
How to set up Google Tag Manager on your website
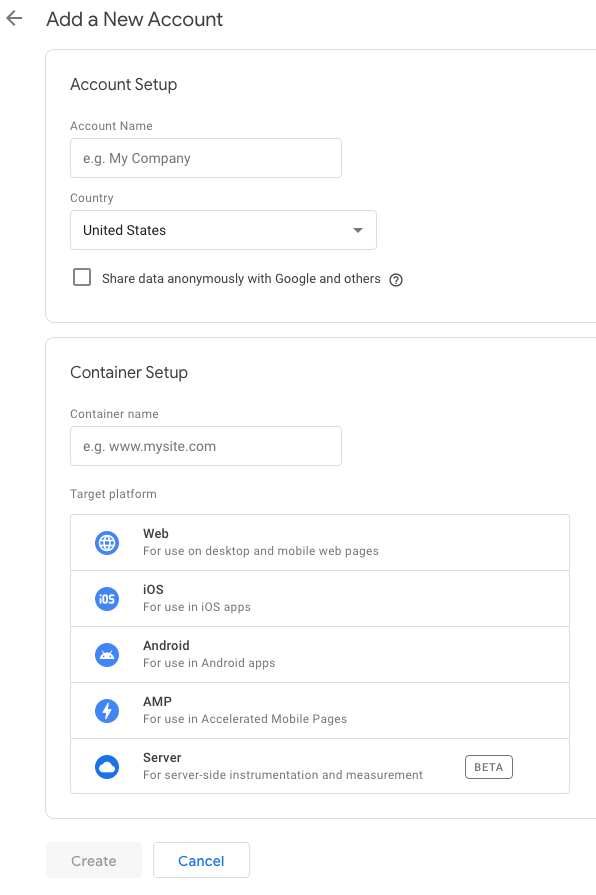
To get started, you’ll need to create a Google Tag Manager account.
- Point your browser to https://tagmanager.google.com and get logged in.
- Click on Create Account
- Enter the name of the account, usually, your company name is fine
- Select the country you’re in
- In the Container name, add your website without the http or https
- Click on Web as the target platform and click Create
- Agree to Google’s terms of service
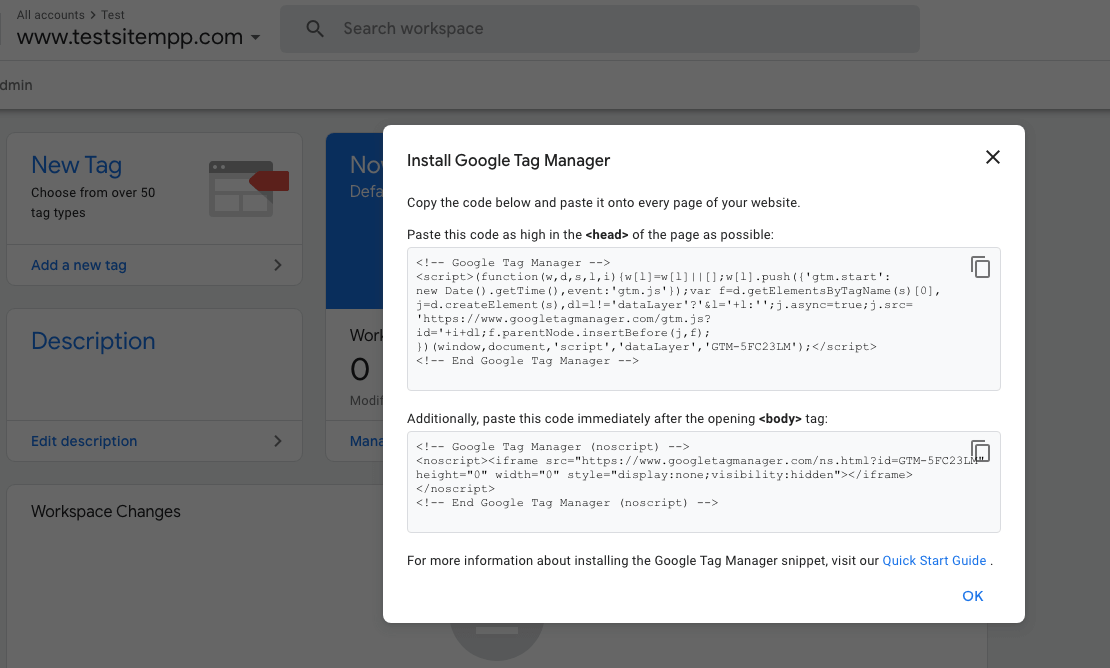
- You’ll be presented with a small code segment you need to install on your site. Follow the instructions.
- When you’re done, click OK
Different platforms for websites have different methods to install Google Tag Manager. In short, follow the directions Google provides.
- Take the larger snippet and place it at the end of the head of your site. Typically, you’ll want GTM on all your pages, so you’ll have to add it to a header file or within the admin of your CMS. Look for this tag </head> and place that large snippet right before it.
- Take the small snippet and place it at the beginning of the body of your site. To get it on all the pages, place it on a header file or within your CMS in the designated area. Look for this tag <body> and place the small snippet right after it.
WordPress and similar CMS’ have a place to insert code into the head and body of the pages. Look for that option in your CMS.
Google Tag Manager is now installed on your site. Next up, let’s get Google Analytics set up inside of Google Tag Manager and test your implementation.